Technology
Quantum Computing in Cambridge: The UK’s Next Tech Revolution

In 2025, Cambridge stands at the forefront of one of the most transformative scientific frontiers of the century: quantum computing. Long regarded as the heart of British research and innovation, the city is rapidly becoming the epicenter of a national effort to develop next-generation computing systems that could redefine global technology. Supported by the UK government’s ambitious innovation strategy and a wave of private investment, Cambridge’s laboratories, universities, and startups are working to turn theoretical breakthroughs into practical applications. This emerging ecosystem is not just advancing quantum science but reshaping how Britain competes in the global technology race.
Breakthrough Research and the Cambridge Advantage
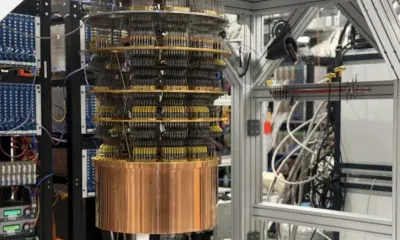
Cambridge has become synonymous with scientific excellence, and quantum computing represents the latest chapter in its storied legacy of discovery. The University of Cambridge, through its Cavendish Laboratory and Quantum Computing Hub, is pioneering research into quantum processors, quantum networking, and error correction systems. These breakthroughs are crucial for overcoming the limitations of classical computing, allowing for calculations that would take today’s supercomputers thousands of years to complete.
Recent experiments have demonstrated significant progress in creating stable quantum bits, or qubits, using trapped ions and photonic systems. Researchers are now developing scalable architectures capable of running real-world algorithms in fields such as drug discovery, materials science, and financial modeling. Quantum communication networks are also under active development, with Cambridge scientists collaborating with the National Physical Laboratory to build secure quantum internet links between research centers.
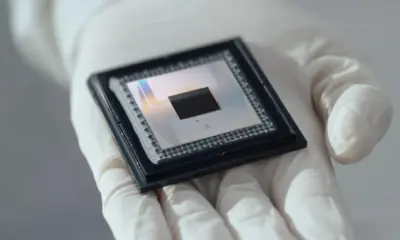
The city’s ecosystem is strengthened by a close relationship between academia and industry. Spin-out companies like Riverlane, Cambridge Quantum, and Orca Computing are translating university research into commercial solutions. These firms are developing software frameworks that make quantum computing accessible to businesses and governments, marking a shift from pure research to applied innovation. Their success demonstrates why Cambridge is often referred to as the “Quantum Valley” of the UK.
Government Strategy and National Investment
The UK government has recognized the transformative potential of quantum computing and has made it a core pillar of its National Innovation Strategy. Earlier this year, officials announced a £3 billion investment package aimed at advancing quantum technologies, including research funding, infrastructure development, and talent programs. This initiative builds on the UK’s existing Quantum Technologies Programme, which has already established a network of research hubs across the country.
The new funding supports projects focused on scaling quantum hardware, improving quantum cryptography, and developing hybrid computing systems that combine quantum and classical processing power. A significant portion of the investment will flow through Cambridge, where government and industry partners are establishing the UK Quantum Campus, a dedicated research and commercialization center designed to accelerate the transition from laboratory to market.
This strategic investment reflects the government’s desire to position Britain as a global leader in deep technology. By aligning public funding with private sector participation, policymakers aim to ensure that breakthroughs made in British laboratories lead to tangible economic benefits. The initiative also emphasizes skills development, with new training programs in universities designed to prepare a generation of engineers, physicists, and software developers for careers in quantum technology.
Private Sector Momentum and Global Partnerships
Alongside government efforts, private investment in quantum computing has surged. Venture capital firms and multinational corporations are increasingly looking to Cambridge as a base for research collaborations and pilot projects. Tech giants have opened partnerships with local startups to explore applications ranging from cybersecurity and logistics optimization to artificial intelligence acceleration.
These partnerships highlight the commercial potential of quantum computing in solving problems that are currently intractable for classical systems. Financial institutions are testing quantum algorithms to improve portfolio management and risk analysis. Pharmaceutical companies are exploring how quantum simulations can accelerate drug discovery. Meanwhile, the energy sector is investigating quantum-based modeling to optimize renewable energy grids.
Cambridge’s international connections further enhance its global relevance. Collaborative agreements with research institutions in the United States, Germany, and Japan ensure that British scientists remain at the cutting edge of quantum innovation. The UK’s participation in multinational initiatives on quantum security also reflects a growing diplomatic emphasis on technological cooperation as a form of strategic influence.
Challenges and the Road to Commercial Reality
Despite rapid progress, significant challenges remain before quantum computing reaches full commercial maturity. Building systems with stable and scalable qubits continues to be a complex scientific hurdle. Quantum decoherence, the loss of quantum information due to environmental interference, remains a major technical obstacle. Researchers in Cambridge are focusing on new error correction codes and materials science innovations to improve system reliability.
Another challenge lies in integrating quantum technology into existing industries. Many organizations lack the expertise to understand how quantum computing can be applied to their specific operations. To address this, the UK government and universities are developing education programs and innovation clusters that connect researchers with businesses eager to explore early adoption.
The race for quantum supremacy is also intensifying globally. The United States, China, and members of the European Union are investing heavily in their own programs. Cambridge’s strength lies in its collaborative model and emphasis on ethical innovation, ensuring that technological advances align with societal needs and responsible use.
Conclusion
Quantum computing in Cambridge represents more than a technological breakthrough, it is a defining moment for the UK’s innovation identity. Through world-class research, strong public investment, and growing private partnerships, the city has positioned itself as a global center for one of the most promising scientific revolutions of the modern era.
If current progress continues, the work being done in Cambridge could fundamentally reshape industries, strengthen national security, and drive economic transformation across the country. The UK’s balanced strategy of fostering innovation while maintaining public accountability offers a blueprint for how nations can lead in the next wave of technological progress. The quantum revolution has begun, and Cambridge is at its very core.